Research Launched to Develop a Monitoring Framework for Antimicrobial Resistance and Antimicrobial Agents in Aquatic Environments — A New Approach to Public Health and Environmental Conservation from a One Health Perspective —
Dec 26, 2025
A research project has been launched, led by a team from Kanazawa University, University of Yamanashi, and the National Institute for Environmental Studies, in collaboration with seven universities and research institutes across Japan—The University of Tokyo, Ehime University, Tohoku University, Kyoto University, Kitasato University, Kochi University, and the National Institute of Health Sciences. The research group has begun work on the study titled “Research Toward the Development of a Monitoring Framework for Antimicrobial Resistance and Antimicrobial Agents in the Environment.” This research project was selected as a Strategic Research and Development initiative (SII-12) under the FY2025 Environmental Research and Technology Development Fund of the Environmental Restoration and Conservation Agency of Japan, and officially commenced on April 1, 2025.
This project aims to clarify the mechanism of spread of antimicrobial resistance through the environment and to establish a sustainable monitoring system.
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR)(*1) is an issue that the World Health Organization (WHO) has warned about as one of the “10 threats to global health,” and the spread of drug resistance through the environment is of particular concern worldwide. In recent years, while countermeasures against antimicrobial resistance have been promoted in the medical and livestock industries, it has been pointed out that drug-resistant bacteria and antimicrobial agents released into the environment through human and animal activities may spread through water and soil. Quantifying the dynamics of antimicrobial resistance in the environment is essential for public health and ecosystem conservation, but until now, a comprehensive monitoring system has not been established. In this project, from the perspective of “One Health” (*2) , we will establish an effective monitoring index and a foundation for countermeasures through an integrated assessment of the sources, spread routes, and environmental impact of antimicrobial resistance, with a focus on public water bodies.
【Outline of Adopted Proposals】
– Call for Proposals: Strategic Research and Development initiative (SII-12) under the FY2025 Environmental Research and Technology Development Fund (II)
– Adopted Project Title: SII-12 “Research Toward the Development of a Monitoring Framework for Antimicrobial Resistance and Antimicrobial Agents in the Environment”
– Project Leader: Professor Ryo Honda (Faculty of Geosciences and Civil Engineering, Institute of Science and Engineering, Kanazawa University)
– Research Period: April 2025 – March 2028
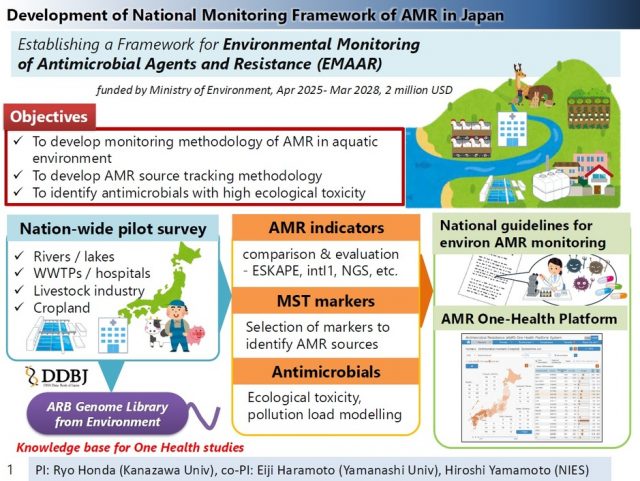 Figure: Conceptual Diagram of This Research Project
Figure: Conceptual Diagram of This Research Project
【Glossary】
*1: Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR)
Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) refers to the phenomenon in which pathogens such as bacteria and viruses develop resistance to antimicrobial agents, including antibiotics, making treatments less effective. As a result, infections may no longer respond to standard therapies, potentially leading to more severe illness or increased risk of death.
*2: One Health
Based on the concept that the health of humans, animals, and the environment are closely interconnected, this approach aims to protect public health and ecosystems through cross-sectoral collaboration. It is promoted by international organizations such as the World Health Organization (WHO), the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), the World Organisation for Animal Health (WOAH), and the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP). This concept is considered essential for addressing global health challenges, including antimicrobial resistance and emerging infectious diseases.
【Related website】
●New Projects Selected for the FY2025 Environmental Research and Technology Development Fund (Press Release by the Environmental Restoration and Conservation Agency, March 14, 2025)
●One Health Platform for Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR)
Researcher’s Information:Ryo Honda

